
Gonadorelin (also referred to as Gonadorelin Acetate) is a synthetically produced gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH). Gonadorelin primarily stimulates the synthesis and release of luteinizing hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary gland. Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) production and release is also increased by gonadorelin, but to a lesser degree. In prepubertal females and some gonadal function disorders, the FSH response may be greater than the LH response.
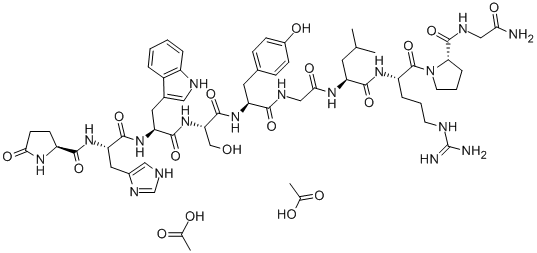
Sequence: Pyr-His-Trp-Ser-Tyr-Gly-Leu-Arg-Pro-Gly-NH2
Molecular formula: C59H83N17O17
Molar Mass: 1302.39
CAS number: 71447-49-9
PubChem: 92432
MeSH: melanotan-II
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone, also known as follicle-stimulating hormone–releasing hormone (FSH-RH) or luteinizing hormone–releasing hormone (LHRH), is peptide hormone responsible for stimulating the anterior pituitary to release follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH).GnrH is considered the initial step of thehypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal axis. At the pituitary, GnRH stimulates the synthesis and secretion of the gonadotropins, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), and luteinizing hormone (LH). These processes are controlled by the size and frequency of GnRH pulses, as well as by feedback from androgens and estrogens. Low-frequency GnRH pulses are required for FSH release, whereas high-frequency GnRH pulses stimulate LH pulses in a one to one manner.
GnRH is secreted in the hypophysial portal bloodstream at the median eminence.[1] The portal blood carries the GnRH to the pituitary gland, which contains the gonadotrope cells, where GnRH activates its own receptor, gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor (GnRHR), a seven-transmembrane G-protein-coupled receptor that stimulates the beta isoform of Phosphoinositide phospholipase C, which goes on to mobilize calcium and protein kinase C. This results in the activation of proteins involved in the synthesis and secretion of the gonadotropins LH and FSH. GnRH is degraded by proteolysis within a few minutes.
